Sensors
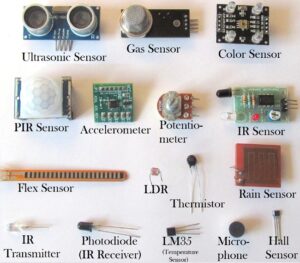
The following is a list of sensor types that may be incorporated into a robot:
- Accelerometer: An accelerometer measures the change of speed of anything that this sensor is mounted on. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Camera: There are a variety of different camera boards used to ‘see’, watch and follow. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices as described in a special project, click here.
- Color: Light is an electromagnetic wave that comes in different wavelengths. These wavelengths in our eyes are transformed into the colors that we see. Photorestor sensors perform color detection. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Compass: A digital compass gives measurements based on the Earth’s magnetic field. They determine north-south-east-west and provide directional guidance for a robot. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Current: A current sensor measures the amount electrical current in use by a particular circuit or device. Electrical current is what is used by all of the various sensors and actuators in a robot and is typically provided by one or more batteries. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Encoder: And encoder is attached to a rotating object and measures its rotation. With that measurement a robot can determine things like velocity, acceleration, angle and displacement. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Infrared Detector: This type of sensor is used for object detectiona and avoidance, and for line following. This sensor has both an emitter and detector. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Load & Torque: There are many different types of force sensors to measure torque and load in mechanical systems. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Photoresitor: A photoresistor measures the presence of light and has a variety of simple applications from turning something on and off to following a light source. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Rangefinder: A rangefinder uses infrared light to measure the distance to an object. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Tactile Bump: This sensor is used for collision detection and push buttons. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Tilt: This sensor measures the tilt of an object that it is attached to based on gravity. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Ultrasonic / Sonor: Sound is emitted and the sound wave is echoed back enabling you to ‘see’ your surroundings. It used for object detection and avoidance, and distance measuring. To learn more about the science and mathematics associated with these types of devices, click here.
- Voice/Speech Recognition: There are a number of different micro-boards that provide voice/speech recognition. Click here for an example of voice/speech recognition board. Coupled with a micro-controller (e.g., Arduino Uno) a set of voice commands can be setup and programmed to control a robot. Click here for a video of a project that demonstrates the use of the board. [Note: We are NOT recommending this specific board since we have NOT used, tested or evaluated it. We are simply showing it since it has reasonably good documentation and demonstration video.]
