- Demonstrate that each key component and/or assemble works the way the manufacturer meant it to work. For example, in a land based self-moving kit, can it go forward, backward, left and right on command. Does it start and stop?
- There is a checklist for each test so the kit builder can track testing progress
- If a test fails, there are written directions on either how to make the appropriate adjustments, perform further tests to determine what caused the problem, and what the kit assembler should do if they cannot successfully resolve the issue
- If a test fails, the test plan indicates what other tests can still be performed to complete as much of the testing before contacting the manufacturer, dealer and/or service company with all of the issues versus one at a time in a serial fashion.
- Extra credit will be given on complicated tests if there are explanations given that describe why the test is being done, why it is important and if there is a range of acceptable results, why it is only those results.
The Kit Testing evaluation is worth 20 points. If there is a test plan, the evaluation score will start with all 20 points. Points will be taken away for incomplete and missing tests, poor documentation, and slow response from the manufacturer, dealer or support organization if/when problems occur. If there is not a formal test plan, points will be awarded on passed tests that have adequate documentation.
[/et_pb_text]STEM Learning / Lessons
Lessons need to be written for the target audience. The introduction to the lessons should identify the target audience characteristics including their age range, background knowledge and robot kit skill level (i.e., beginner/novice, moderate, expert). The introduction should summarize what the student will learn after completing all of the lessons.
Lessons need to be well written and clear. Lessons written in English must be grammatically correct.
Lessons should provide references to background material to enable a student to learn more from in depth information. If a lesson involves complex terms or terminology, a reference glossary must be included.
There should be a lesson for each major function or robot capability. If programming is involved, program code should be clearly documented and follow standard syntax and programming standards. The program code should be consistent across all program files, listings and modules. If complex formulas are used, references to detailed descriptions of how they work must minimally be included.
At the end of all lessons a lesson summary should provide suggestions of what student should pursue next based on their level of interest.
The STEM Sessions evaluation is worth 40 points. It is the most important of all of the sections. Points for Lessons will be both earned and lost. Extra credit will be given for unique and original work.
Summary
The Summary will include all the positive and negative aspects of the kit assembly, testing and learning experience. It will include recommendations on how to improve the kit and the kit building experience, and highlight how a student can continue learning through the use of the kit.
The summary will also include the overall score given to the kit and kit assembly process.
- Easy to read, clear instructions that both tell and show how to do each step
- Parts are well made and fit together cleanly unless documented
- For complicated assemblies, there is a video that shows in detail how things fit together (i.e., kit part explosion) or how to actually assemble key steps. The video(s) should the kit builder to go to the desired section, and to replay it multiple times if need be. It is common to replay complicated assembly processes multiple times and in slow motion.
- Sub-sections of a kit can be assembled and then assembled together into the final robot providing clear stopping points during the assembly process.
- Difficult to install screws, nuts and washers are noted so that those of us with big, clumsy hands and bad eye sight can complete the assembly. We may need better bright light, magnifying glasses and/or tweezers but our expectations have been set by the assembly instructions.
- It is important to identify the more difficult sections and give tips on how to complete the step(s).
- If an estimate is given on how long it takes to complete the kit assembly, include the skill level of the person for which the estimate is given.
- Managing the kit builders expectation is a key element of the overall successful assembly process.
The Kit Assembly evaluation is worth 25 points. Evaluation starts with a zero score and then added and subtracted as the build process progresses. In ability to complete the build process will score 0 points.
[/et_pb_text]Kit Testing
A great kit has a test plan independent of any lesson or instructional documentation. The test plan will:
- Demonstrate that each key component and/or assemble works the way the manufacturer meant it to work. For example, in a land based self-moving kit, can it go forward, backward, left and right on command. Does it start and stop?
- There is a checklist for each test so the kit builder can track testing progress
- If a test fails, there are written directions on either how to make the appropriate adjustments, perform further tests to determine what caused the problem, and what the kit assembler should do if they cannot successfully resolve the issue
- If a test fails, the test plan indicates what other tests can still be performed to complete as much of the testing before contacting the manufacturer, dealer and/or service company with all of the issues versus one at a time in a serial fashion.
- Extra credit will be given on complicated tests if there are explanations given that describe why the test is being done, why it is important and if there is a range of acceptable results, why it is only those results.
The Kit Testing evaluation is worth 20 points. If there is a test plan, the evaluation score will start with all 20 points. Points will be taken away for incomplete and missing tests, poor documentation, and slow response from the manufacturer, dealer or support organization if/when problems occur. If there is not a formal test plan, points will be awarded on passed tests that have adequate documentation.
STEM Learning / Lessons
Lessons need to be written for the target audience. The introduction to the lessons should identify the target audience characteristics including their age range, background knowledge and robot kit skill level (i.e., beginner/novice, moderate, expert). The introduction should summarize what the student will learn after completing all of the lessons.
Lessons need to be well written and clear. Lessons written in English must be grammatically correct.
Lessons should provide references to background material to enable a student to learn more from in depth information. If a lesson involves complex terms or terminology, a reference glossary must be included.
There should be a lesson for each major function or robot capability. If programming is involved, program code should be clearly documented and follow standard syntax and programming standards. The program code should be consistent across all program files, listings and modules. If complex formulas are used, references to detailed descriptions of how they work must minimally be included.
At the end of all lessons a lesson summary should provide suggestions of what student should pursue next based on their level of interest.
The STEM Sessions evaluation is worth 40 points. It is the most important of all of the sections. Points for Lessons will be both earned and lost. Extra credit will be given for unique and original work.
Summary
The Summary will include all the positive and negative aspects of the kit assembly, testing and learning experience. It will include recommendations on how to improve the kit and the kit building experience, and highlight how a student can continue learning through the use of the kit.
The summary will also include the overall score given to the kit and kit assembly process.
A great kit to assemble is one with:
- Easy to read, clear instructions that both tell and show how to do each step
- Parts are well made and fit together cleanly unless documented
- For complicated assemblies, there is a video that shows in detail how things fit together (i.e., kit part explosion) or how to actually assemble key steps. The video(s) should the kit builder to go to the desired section, and to replay it multiple times if need be. It is common to replay complicated assembly processes multiple times and in slow motion.
- Sub-sections of a kit can be assembled and then assembled together into the final robot providing clear stopping points during the assembly process.
- Difficult to install screws, nuts and washers are noted so that those of us with big, clumsy hands and bad eye sight can complete the assembly. We may need better bright light, magnifying glasses and/or tweezers but our expectations have been set by the assembly instructions.
- It is important to identify the more difficult sections and give tips on how to complete the step(s).
- If an estimate is given on how long it takes to complete the kit assembly, include the skill level of the person for which the estimate is given.
- Managing the kit builders expectation is a key element of the overall successful assembly process.
The Kit Assembly evaluation is worth 25 points. Evaluation starts with a zero score and then added and subtracted as the build process progresses. In ability to complete the build process will score 0 points.
[/et_pb_text]Kit Testing
A great kit has a test plan independent of any lesson or instructional documentation. The test plan will:
- Demonstrate that each key component and/or assemble works the way the manufacturer meant it to work. For example, in a land based self-moving kit, can it go forward, backward, left and right on command. Does it start and stop?
- There is a checklist for each test so the kit builder can track testing progress
- If a test fails, there are written directions on either how to make the appropriate adjustments, perform further tests to determine what caused the problem, and what the kit assembler should do if they cannot successfully resolve the issue
- If a test fails, the test plan indicates what other tests can still be performed to complete as much of the testing before contacting the manufacturer, dealer and/or service company with all of the issues versus one at a time in a serial fashion.
- Extra credit will be given on complicated tests if there are explanations given that describe why the test is being done, why it is important and if there is a range of acceptable results, why it is only those results.
The Kit Testing evaluation is worth 20 points. If there is a test plan, the evaluation score will start with all 20 points. Points will be taken away for incomplete and missing tests, poor documentation, and slow response from the manufacturer, dealer or support organization if/when problems occur. If there is not a formal test plan, points will be awarded on passed tests that have adequate documentation.
STEM Learning / Lessons
Lessons need to be written for the target audience. The introduction to the lessons should identify the target audience characteristics including their age range, background knowledge and robot kit skill level (i.e., beginner/novice, moderate, expert). The introduction should summarize what the student will learn after completing all of the lessons.
Lessons need to be well written and clear. Lessons written in English must be grammatically correct.
Lessons should provide references to background material to enable a student to learn more from in depth information. If a lesson involves complex terms or terminology, a reference glossary must be included.
There should be a lesson for each major function or robot capability. If programming is involved, program code should be clearly documented and follow standard syntax and programming standards. The program code should be consistent across all program files, listings and modules. If complex formulas are used, references to detailed descriptions of how they work must minimally be included.
At the end of all lessons a lesson summary should provide suggestions of what student should pursue next based on their level of interest.
The STEM Sessions evaluation is worth 40 points. It is the most important of all of the sections. Points for Lessons will be both earned and lost. Extra credit will be given for unique and original work.
Summary
The Summary will include all the positive and negative aspects of the kit assembly, testing and learning experience. It will include recommendations on how to improve the kit and the kit building experience, and highlight how a student can continue learning through the use of the kit.
The summary will also include the overall score given to the kit and kit assembly process.
Before assembling any kits, a quick reading of the instructions and an inventory of the parts should be made. The following are key to a great kit and kit assembly experience:
- Do the instructions include a detailed list of the parts with counts of the individual parts?
- Are the parts instructions clear and readable?
- For similar and complicated parts, are there pictures, diagrams and/or labels that identify each part?
- Are like parts (e.g., screws, nuts, washers) in their own bags or containers with easy-to-read labels?
- With parts that have a specific orientation in the assembled kit (e.g., top, bottom, left and right side) is the part orientation clearly labeled?
- Some parts need to be tested before assembly. Are these parts properly labeled and the test with success criteria clearly described?
- Are all of the parts included?
- For very small parts that are difficult to install (e.g., tiny screws and nuts), are there extra in case one/some are dropped and lost?
- For large, complicated kits is there a description of how the parts should be organized and laid out to make the assembly process easier and helpful in avoiding assembly mistakes?
The Parts Inventory evaluation is worth 15 points. Scoring in this section starts with 15 points. If one of the criteria is not met, one or more points is deducted from the score. It is possible to end up with a negative score.
[/et_pb_text]Kit Assembly
A great kit to assemble is one with:
- Easy to read, clear instructions that both tell and show how to do each step
- Parts are well made and fit together cleanly unless documented
- For complicated assemblies, there is a video that shows in detail how things fit together (i.e., kit part explosion) or how to actually assemble key steps. The video(s) should the kit builder to go to the desired section, and to replay it multiple times if need be. It is common to replay complicated assembly processes multiple times and in slow motion.
- Sub-sections of a kit can be assembled and then assembled together into the final robot providing clear stopping points during the assembly process.
- Difficult to install screws, nuts and washers are noted so that those of us with big, clumsy hands and bad eye sight can complete the assembly. We may need better bright light, magnifying glasses and/or tweezers but our expectations have been set by the assembly instructions.
- It is important to identify the more difficult sections and give tips on how to complete the step(s).
- If an estimate is given on how long it takes to complete the kit assembly, include the skill level of the person for which the estimate is given.
- Managing the kit builders expectation is a key element of the overall successful assembly process.
The Kit Assembly evaluation is worth 25 points. Evaluation starts with a zero score and then added and subtracted as the build process progresses. In ability to complete the build process will score 0 points.
Kit Testing
A great kit has a test plan independent of any lesson or instructional documentation. The test plan will:
- Demonstrate that each key component and/or assemble works the way the manufacturer meant it to work. For example, in a land based self-moving kit, can it go forward, backward, left and right on command. Does it start and stop?
- There is a checklist for each test so the kit builder can track testing progress
- If a test fails, there are written directions on either how to make the appropriate adjustments, perform further tests to determine what caused the problem, and what the kit assembler should do if they cannot successfully resolve the issue
- If a test fails, the test plan indicates what other tests can still be performed to complete as much of the testing before contacting the manufacturer, dealer and/or service company with all of the issues versus one at a time in a serial fashion.
- Extra credit will be given on complicated tests if there are explanations given that describe why the test is being done, why it is important and if there is a range of acceptable results, why it is only those results.
The Kit Testing evaluation is worth 20 points. If there is a test plan, the evaluation score will start with all 20 points. Points will be taken away for incomplete and missing tests, poor documentation, and slow response from the manufacturer, dealer or support organization if/when problems occur. If there is not a formal test plan, points will be awarded on passed tests that have adequate documentation.
STEM Learning / Lessons
Lessons need to be written for the target audience. The introduction to the lessons should identify the target audience characteristics including their age range, background knowledge and robot kit skill level (i.e., beginner/novice, moderate, expert). The introduction should summarize what the student will learn after completing all of the lessons.
Lessons need to be well written and clear. Lessons written in English must be grammatically correct.
Lessons should provide references to background material to enable a student to learn more from in depth information. If a lesson involves complex terms or terminology, a reference glossary must be included.
There should be a lesson for each major function or robot capability. If programming is involved, program code should be clearly documented and follow standard syntax and programming standards. The program code should be consistent across all program files, listings and modules. If complex formulas are used, references to detailed descriptions of how they work must minimally be included.
At the end of all lessons a lesson summary should provide suggestions of what student should pursue next based on their level of interest.
The STEM Sessions evaluation is worth 40 points. It is the most important of all of the sections. Points for Lessons will be both earned and lost. Extra credit will be given for unique and original work.
Summary
The Summary will include all the positive and negative aspects of the kit assembly, testing and learning experience. It will include recommendations on how to improve the kit and the kit building experience, and highlight how a student can continue learning through the use of the kit.
The summary will also include the overall score given to the kit and kit assembly process.
Evaluation and Scoring Overview
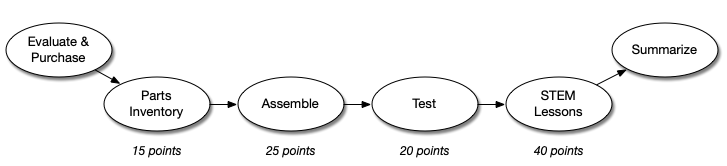
Amblit Technologies is using a six (6) step robot STEM kit evaluation and scoring process as depicted in the diagram above. Four (4) of the six (6) earn up to a total of 100 points. All steps, even those without points, are scored on 0 (terrible) to 10 (great) experience score. For a kit to earn all 100 points, they need a 10 evaluation score on the steps with points.
Evaluation & Purchase
Amblit Technologies is continually surveying the available robot STEM kits across different retail outlets and manufacturer stores. Ideally we would like to find, buy and evaluate a representative kit from all the manufacturers of robot STEM kits that are either computer or programmable controller based, and cost less than $1,000. We will make exceptions from time to time. We also accept requests, which are then added to our initial evaluation queue. Currently we don’t have a limit on the number of kits and their supporting accessories (computer, batteries, …) that we will purchase, but we currently support only five (5) active kit evaluations at a time.
We are NOT participating in any affiliate marketing or manufacturer programs so as to remove any potential bias that may enter into our evaluations, unlike other review and recommendation websites, videos and influencers. Again, our goal is to recommend the best possible experiences for students and teachers, while helping manufacturers improve their offerings and substantially improve the STEM learning possibilities.
Every kit after purchase starts with a zero (0) score, even if we have had difficulty in making the purchase or obtaining any required accessories (e.g., batteries, computers).
Summarizing for a kit to be considered for evaluation:
- Advertised by its manufacturer to be a robot kit that includes some sort of assembly
- Must include either a programmable computer or controller
- Includes STEM related lessons for the kit builder/assembler
From time to time we will consider and review other types of related products, devices and kits that are related to robot STEM kits.
Parts Inventory
Before assembling any kits, a quick reading of the instructions and an inventory of the parts should be made. The following are key to a great kit and kit assembly experience:
- Do the instructions include a detailed list of the parts with counts of the individual parts?
- Are the parts instructions clear and readable?
- For similar and complicated parts, are there pictures, diagrams and/or labels that identify each part?
- Are like parts (e.g., screws, nuts, washers) in their own bags or containers with easy-to-read labels?
- With parts that have a specific orientation in the assembled kit (e.g., top, bottom, left and right side) is the part orientation clearly labeled?
- Some parts need to be tested before assembly. Are these parts properly labeled and the test with success criteria clearly described?
- Are all of the parts included?
- For very small parts that are difficult to install (e.g., tiny screws and nuts), are there extra in case one/some are dropped and lost?
- For large, complicated kits is there a description of how the parts should be organized and laid out to make the assembly process easier and helpful in avoiding assembly mistakes?
The Parts Inventory evaluation is worth 15 points. Scoring in this section starts with 15 points. If one of the criteria is not met, one or more points is deducted from the score. It is possible to end up with a negative score.
Kit Assembly
A great kit to assemble is one with:
- Easy to read, clear instructions that both tell and show how to do each step
- Parts are well made and fit together cleanly unless documented
- For complicated assemblies, there is a video that shows in detail how things fit together (i.e., kit part explosion) or how to actually assemble key steps. The video(s) should the kit builder to go to the desired section, and to replay it multiple times if need be. It is common to replay complicated assembly processes multiple times and in slow motion.
- Sub-sections of a kit can be assembled and then assembled together into the final robot providing clear stopping points during the assembly process.
- Difficult to install screws, nuts and washers are noted so that those of us with big, clumsy hands and bad eye sight can complete the assembly. We may need better bright light, magnifying glasses and/or tweezers but our expectations have been set by the assembly instructions.
- It is important to identify the more difficult sections and give tips on how to complete the step(s).
- If an estimate is given on how long it takes to complete the kit assembly, include the skill level of the person for which the estimate is given.
- Managing the kit builders expectation is a key element of the overall successful assembly process.
The Kit Assembly evaluation is worth 25 points. Evaluation starts with a zero score and then added and subtracted as the build process progresses. In ability to complete the build process will score 0 points.
Kit Testing
A great kit has a test plan independent of any lesson or instructional documentation. The test plan will:
- Demonstrate that each key component and/or assemble works the way the manufacturer meant it to work. For example, in a land based self-moving kit, can it go forward, backward, left and right on command. Does it start and stop?
- There is a checklist for each test so the kit builder can track testing progress
- If a test fails, there are written directions on either how to make the appropriate adjustments, perform further tests to determine what caused the problem, and what the kit assembler should do if they cannot successfully resolve the issue
- If a test fails, the test plan indicates what other tests can still be performed to complete as much of the testing before contacting the manufacturer, dealer and/or service company with all of the issues versus one at a time in a serial fashion.
- Extra credit will be given on complicated tests if there are explanations given that describe why the test is being done, why it is important and if there is a range of acceptable results, why it is only those results.
The Kit Testing evaluation is worth 20 points. If there is a test plan, the evaluation score will start with all 20 points. Points will be taken away for incomplete and missing tests, poor documentation, and slow response from the manufacturer, dealer or support organization if/when problems occur. If there is not a formal test plan, points will be awarded on passed tests that have adequate documentation.
STEM Learning / Lessons
Lessons need to be written for the target audience. The introduction to the lessons should identify the target audience characteristics including their age range, background knowledge and robot kit skill level (i.e., beginner/novice, moderate, expert). The introduction should summarize what the student will learn after completing all of the lessons.
Lessons need to be well written and clear. Lessons written in English must be grammatically correct.
Lessons should provide references to background material to enable a student to learn more from in depth information. If a lesson involves complex terms or terminology, a reference glossary must be included.
There should be a lesson for each major function or robot capability. If programming is involved, program code should be clearly documented and follow standard syntax and programming standards. The program code should be consistent across all program files, listings and modules. If complex formulas are used, references to detailed descriptions of how they work must minimally be included.
At the end of all lessons a lesson summary should provide suggestions of what student should pursue next based on their level of interest.
The STEM Sessions evaluation is worth 40 points. It is the most important of all of the sections. Points for Lessons will be both earned and lost. Extra credit will be given for unique and original work.
Summary
The Summary will include all the positive and negative aspects of the kit assembly, testing and learning experience. It will include recommendations on how to improve the kit and the kit building experience, and highlight how a student can continue learning through the use of the kit.
The summary will also include the overall score given to the kit and kit assembly process.
